In this post, we seek to clarify the concepts of accountability, responsibility and authority. These terms have specific meanings; the concepts are frequently confused. Lack of clarity can result in micro-management.
In the next post, we will explore challenges related to making school leaders accountable for school performance.
Accountability
Let’s begin with a definition.
Accountability: the collection of outcomes that an individual is charged to produce and for which the individual can be held to account
Outcome based
Most individuals in organisations are charged with achieving certain outcomes, their accountabilities.
Negotiated
The outcomes for which an individual is held to account are usually determined through a process of negotiation. The head of a government agency negotiates with their respective government Minister. A chief executive negotiates with their Board. A principal negotiates with the district superintendent, or equivalent.
Outcomes are monitored and reported
Once agreed, progress towards the agreed outcomes is monitored and reported. The most senior people in organisations are held to account for the outcomes achieved by their organisation. This does not mean they are expected to achieve these outcomes on their own; they must work with others in the organisation to achieve their accountabilities.
Cannot be delegated
In a corporate context, a chief executive can negotiate with the chief financial officer, for example, the range of outcomes for which the chief financial officer agrees to be held to account. This is likely to include an accountability that the financial accounts are kept in accordance with relevant laws and accounting standards. The chief executive officer is not absolved from her accountability to ensure that the organisation complies with all relevant laws. The most senior executives remain accountable for the organisation’s performance. This is true even when failure to meet agreed outcomes is the result of someone further down the organisation failing to meet their accountabilities.
In a school context, principals are frequently held to account for student learning outcomes. This accountability is negotiated with their line manager and cannot be delegated. The principal must work with teaching staff to achieve this accountability.
In practice, the negotiation of accountabilities is frequently lost to the history of an organisation. The accountabilities associated with particular roles in the organisation were negotiated long ago and are now accepted as part of that job description. Under these circumstances, there is no fresh negotiation with a new incumbent for a position, rather, the accountabilities are accepted with the job.
Can be accepted
Achievement of outcomes, and thus achievement of accountabilities, is contingent upon the quality of the organisation’s systems and process, as was described in detail in chapter three of our book Improving Learning. The senior executive of the organisation is thus accountable for the performance of all the organisation’s key systems and processes. To manage this accountability in a practical manner, she negotiates for others to accept accountability for specific organisational processes. For example, a principal may negotiate with a deputy for the deputy to accept accountability for the student discipline and welfare processes. Similarly, the school leaders negotiate with classroom teachers the outcomes for which the teachers will be held accountable.
Accountability defines who is to be held to account for the achievement of outcomes.
Responsibility
Accountabilities are achieved through meeting responsibilities.
Responsibility: the work activities and outputs an individual is charged to complete.
Process based
The outcomes for which an organisation strives are achieved through enacting processes. Individuals within the organisation complete their work activities, which, in turn, link together as the organisation’s processes. These processes may be documented as deployment flowcharts that make explicit the responsibilities of those charged with enacting the process steps.
Can be delegated
Responsibilities can be delegated. The principal may, for example, ask the deputy principal to run a staff meeting. A teacher may ask an aide to prepare learning materials. The office manager may delegate responsibility for stationery supplies to an assistant.
When a responsibility is delegated, the accountability for the outcome is not.
Distinct from accountability
At senior levels of an organisation, accountabilities and responsibilities may be significantly different. Senior executives remain accountable for many things upon which they take no action on a day-to-day basis. A school principal remains accountable for the safety and wellbeing of all students in the school, yet has little day-to-day responsibility for sickbay, for example.
At more junior levels, the division between accountabilities and responsibilities becomes less distinct. A classroom teacher is typically responsible for the learning and teaching programs of her classes; the teacher is also accountable for the outcomes of those programs.
Responsibility defines who will undertake specific processes and actions.
Documenting Accountability and Responsibility
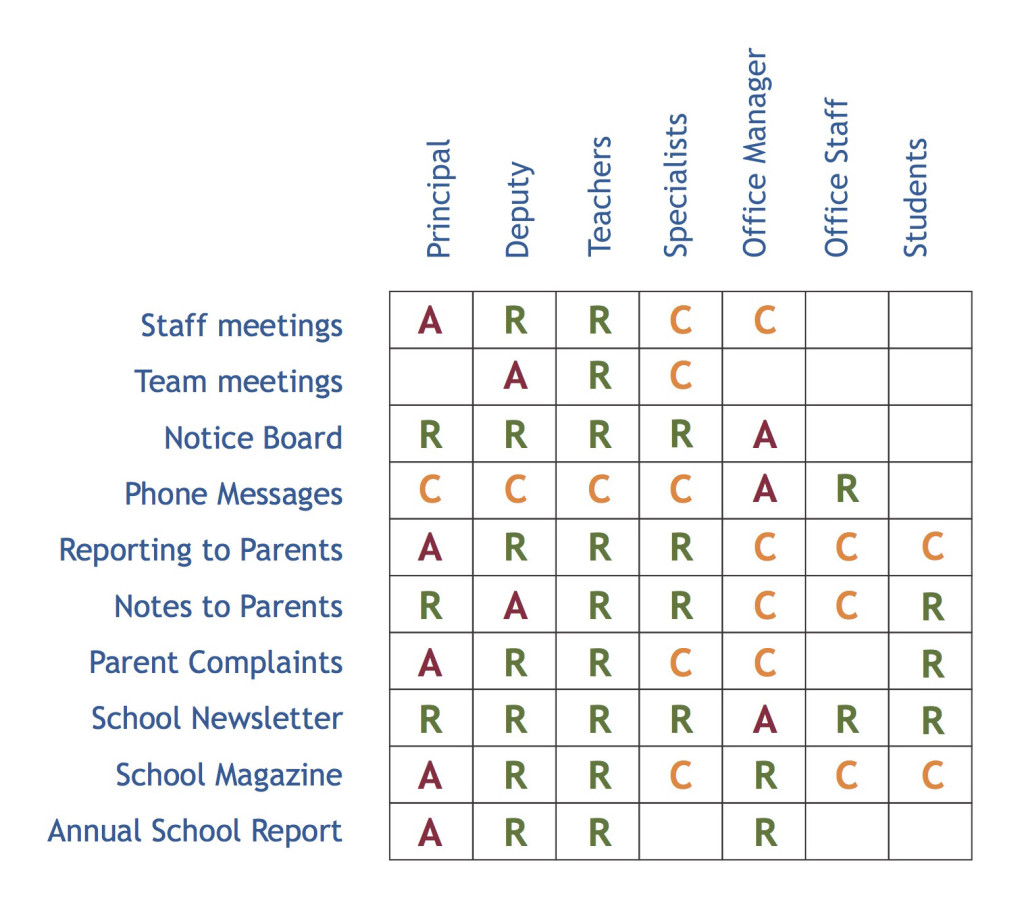
A Process Accountability Matrix may be used to document agreements regarding accountabilities and responsibilities. Key processes are listed in the rows of the matrix and roles identified in the columns. Within each cell of the matrix, the role may be listed as:
- Accountable for outcomes of the process.
- Responsible for performing actions within the process.
- Consulted or informed during execution of the process.
A Process Accountability Matrix can be used to ensure there are no gaps or overlaps in accountability, i.e. each process has one and only one role Accountable for the process. The matrix can also identify roles that have little or too much responsibility and accountability.
Authority
Any discussion of accountability and responsibility is incomplete if it does not also discuss authority.
Authority: the delegated right to make decisions
Decision based
It is important to be clear who is accountable for outcomes and who is responsible for actions. It is equally important to ensure that appropriate authority is delegated; who is authorised to make decisions?
Governments define the structures by which decisions will be made and disputes settled. These delegations are detailed in legislation and regulations. Law enforcement agencies, such as the police, are established to enforce the determinations. Courts are also established to adjudicate disputes.
Delegated
Governments also delegate specific rights to manage and regulate public institutions, including schools. These rights can be delegated to government agencies, and they can also be delegated to non-government agencies such as religious authorities. These agencies and authorities, in turn, delegate specific rights to officials, including school leaders. Through this process of delegation, school leaders have rights to make defined determinations for the school. The specific rights delegated to school leaders vary by jurisdiction. In some cases, school leaders have the right to hire and fire; some have the authority to manage the whole-of-school budget. In other cases, the school principal has significantly less authority.
Authority can be delegated.
Supports responsibility and accountability
Responsibility must be accompanied by authority to make decisions and take action. The school principal can authorise the bursar or business manager to keep financial records and to pay accounts, which is consistent with the bursar’s responsibilities. The office manager may have the responsibility and authority to enrol students. Teachers have the authority and responsibility to report on students’ progress.
Similarly, the negotiation and acceptance of accountability needs to be accompanied by the agreement to delegate the necessary authority to meet those accountabilities. For example, if a deputy principal accepts the accountability of ensuring that school programs comply with the requirements of a national curriculum, they will also need the authority to establish school policies and procedures to ensure this accountability is met.
Avoids micro-mangement
Where authority is not aligned with accountabilities and responsibilities there will be frustration and wasted effort.
Where there is a failure to clearly delegate authority, organisations can become paralysed. If an officer is unsure if they have the authority to make a decision, they will push the decision ‘up the line’. This results in delays and frustration. It also frequently results in more senior leaders’ time being taken up with decisions that could and should have been made at more appropriate levels in the organisation.
Micro-management is a failure to effectively delegate authority.
As is the case with accountabilities and responsibilities, the establishment of delegated authorities is also frequently lost to the history of the organisation, and simply accepted as inherent in the job description.
Authority defines who has the right to make decisions.
See an example of a school Process Accountability Matrix.
Learn more about managing processes, and process accountability, from our Learning and Improvement Guide: Process Mapping.
Note: this post draws heavily upon the teachings of Homer Sarasohn. The full text of “The Fundamentals of Industrial Management” (1949) by Sarasohn and Protozoan.
I am grateful to my friend and colleague, Norbert Vogel, for his helpful comments on an early draft of this post.


